Labs MPLS
MPLS Lab Overview (Juniper ACX1100 with Logical Systems)
A lab environment designed to test MPLS functionality, logical systems isolation, VLAN-based customer separation, and traffic engineering using multiple core paths.
Note: Most of the provided labs are automated using Ansible. However, for educational purposes, we will provide only Junos configuration examples.
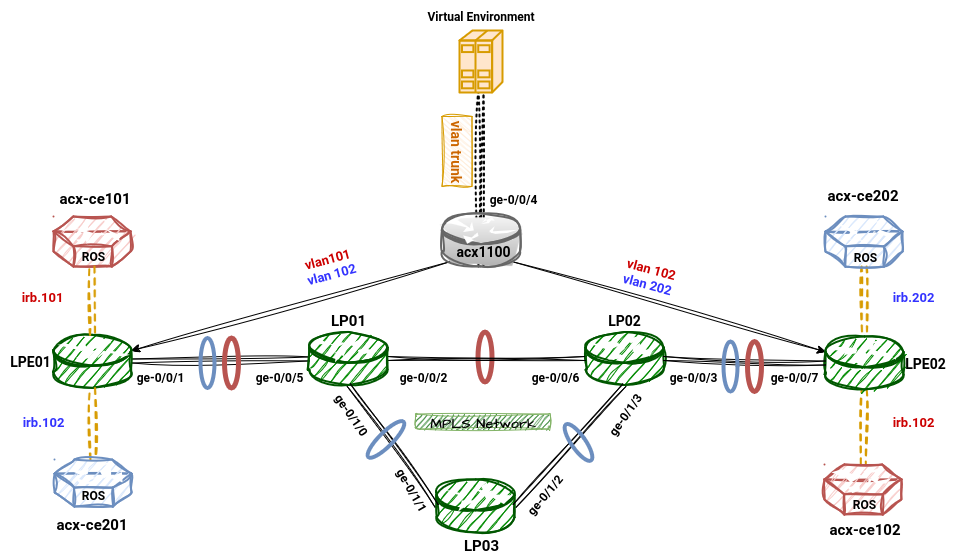
Components
- ACX1100: Physical Juniper router hosting all logical systems (LS).
- LP01, LP02, LP03: Core MPLS logical systems forming a ring topology (Core).
- LPE01, LPE02: Provider Edge (PE) logical systems connecting to CE devices via VLANs.
- CE Devices (ROS): 4 virtual machines acting as customer edge routers (connected via VLAN subinterfaces).
Connectivity
- Interface
ge-0/0/4: Trunk port connecting ACX1100 to a virtual environment (ROS VMs), carrying:- VLAN 101 →
acx-ce101(Customer A) - VLAN 102 →
acx-ce102(Customer A) - VLAN 201 →
acx-ce201(Customer B) - VLAN 202 →
acx-ce202(Customer B)
- VLAN 101 →
-
VLAN subinterfaces are mapped to specific logical systems (
lpe01,lpe02) based on customer. - Core connectivity:
lpe01↔lp01lpe02↔lp02lp01,lp02,lp03form an MPLS ring.
Traffic Engineering Paths
- 🔴 Red path: LP01 → LP02
- 🔵 Blue path: LP01 → LP03 → LP02
Used for demonstrating MPLS TE or LSP failover/optimization.
Use Case Highlights
- L3VPN or L2VPN customer separation
- Redundant TE path testing
- VLAN-to-LS mapping demonstration
- CE-to-CE communication across PE routers
Juniper ACX1100 – MPLS Feature Overview
The Juniper ACX1100 supports advanced MPLS features, allowing service providers to extend MPLS-based services closer to the customer edge.
Supported MPLS Features
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| MPLS Forwarding | Hardware-based, line-rate MPLS label switching |
| LDP (Label Distribution Protocol) | Dynamically distributes MPLS labels over IGP (OSPF/IS-IS) |
| RSVP-TE | Traffic-engineered LSPs with bandwidth reservation and constraints |
| Static LSPs | Manually configured LSPs for simple MPLS forwarding |
| BGP/MPLS L3VPN | Full support for RFC 4364-based Layer 3 VPN services |
| BGP-based L2VPN (RFC 6624) | Limited support for point-to-point Ethernet VPNs using BGP signaling |
| PWE (T-LDP) | Pseudowire Emulation over targeted LDP for Ethernet over MPLS (E-Line) |
MPLS Limitations
| Unsupported Feature | Notes |
|---|---|
| VPLS (LDP or BGP autodiscovery) | Not supported – lacks MAC learning and control plane functions required for multipoint Ethernet VPNs |
| EVPN (Ethernet VPN) | Not supported – no VXLAN or EVPN bridging capabilities |
| Komplla L2VPN | Not supported – only basic BGP-signaled E-Line L2VPNs are available |
| MAC Learning over Pseudowires | Not supported – limits use to E-Line type services only |
Notes
- While some older documentation suggests no L2VPN support, the official datasheet confirms BGP-based L2VPN and T-LDP pseudowire support.
- Ensure you’re running a supported Junos OS version (typically 14.x or later) to access all MPLS capabilities.
- Not suitable for full VPLS or EVPN-based service designs – consider ACX4000 or MX Series for those roles.